In Argentina and Chile, Grupo Calidra Cono Sur is a vital ally of potabilization and purification plants that require lime to treat drinking water, hygiene, and domestic and industrial effluents. Why is it a fundamental input to reverse global water stress?
By Grupo Calidra
Access to water is an essential human right. As the world population grows and the impact of climate change worsens, there is an increasing urgency to balance commercial demands for water resources with the requirement that communities be supplied with potable water to meet basic needs.
March 22 is celebrated as World Water Day. The United Nations established it in 1993 to raise awareness and mobilize actions to address the global water and sanitation crisis, as 2 billion people still live without access to safe drinking water.
This year, the theme of the day is "Water for Peace," under the idea that when water is scarce or contaminated, or when people have unequal or no access, tensions between communities and countries increase.
One of the central axes for the UN revolves around supporting the achievement of Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) number 6: Water and Sanitation for All by 2030. Because equitable water management is essential for socioeconomic development, for the production of energy and food, public health, and adaptation to climate change. Ultimately, it is a decisive link between society and the environment.
In Argentina, according to data from the 2022 CENSUS, there are more than 500 thousand people who do not have access to safe drinking water. And that number is likely higher, as many Argentine households access water through secondary sources (cistern, ditch, rainwater, river), and it is not specified if these waters undergo approved potabilization treatment.
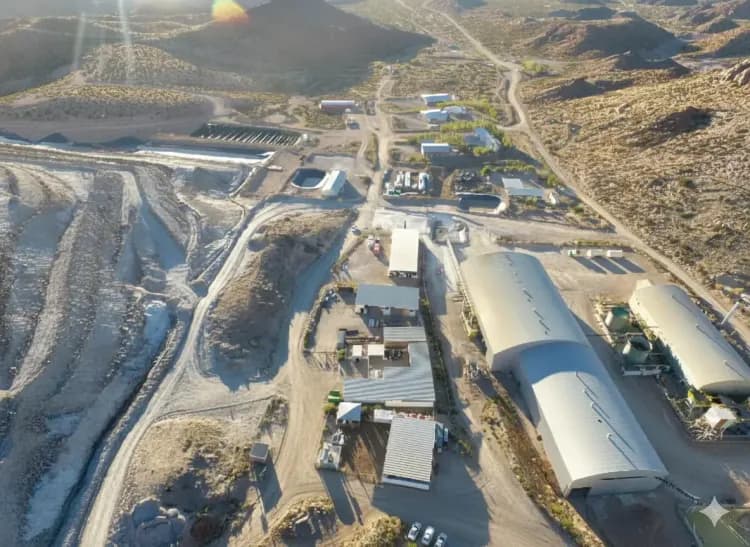
What is clear is that in the most populous cities of Argentina and Chile, Grupo Calidra Cono Sur plays a fundamental strategic role, supplying lime and carbonates to potabilization and purification plants that supply drinking water and treat wastewater.
The World Resources Institute (WRI), a non-profit organization that promotes sustainable management of natural resources, states that the world is undergoing water stress that affects millions of people.
According to the latest report from the Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas elaborated by the WRI (a sort of map that measures global water risk), there are 25 countries - a quarter of the world's population - facing extremely high water stress, and each year they regularly consume almost all their available water supply.
The study revealed another alarming phenomenon: at least 50% of the world's population (around 4 billion people) lives in conditions of severe water scarcity for at least one month per year.
Drinking water and wastewater
On one hand, there is the drinking water we consume. On the other, the water we use for hygiene and sanitation that is then treated. On a human level, ensuring these two accesses to the resource is vital to reduce the global burden of morbidity and improve the health, education, and economic productivity of populations.
And to guarantee the availability of these waters, the intervention of lime is indispensable, as it functions as a pH regulator, coagulant, bacterial inhibitor, stabilizer, and precipitator of contaminants.
Many chemicals participate in the treatment of drinking water and domestic wastewater. Both lime in its variety of variants (calcium oxide, calcium hydroxide) and calcium carbonate act at different stages of the process.
"Many of Calidra's products such as quicklime (Oxid®), hydrated lime (Quimex®), and calcium carbonate are involved in water treatment. Some are used in drinking water treatment and others to treat wastewater. Meanwhile, calcium carbonate is used in the remineralization of desalinated water," explains Melina Berdanelli, Technical Commercial Representative of Grupo Calidra Argentina.
Lime, a multitasking input for healthy water
The main use of lime in the water potabilization process is as a pH regulator. The amount of lime required for this function depends on the type of water to be treated.
As happens in so many industries, lime is much more than a pH regulator. In water treatment, it also acts as a germicide, helps precipitate heavy metals, and promotes the destruction of organic matter present in water, helping to reduce the BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand).
"BOD is related to the amount of organic matter in the water, which serves as a substrate for bacteria and viruses that break it down. Lime destroys that flora and oxidizes the organic matter," explains Laura Correa, Research and Development Manager of Calidra Argentina.
Another function of lime is to help sediment suspended material. Although it is not its main function, other coagulating elements are usually added for this purpose.
"In water, we have different materials: some are in a coarser form like sand, which can precipitate spontaneously without the need for flocculants; others are in a colloidal form, very small particles that do not precipitate on their own. These require flocculation, that is, joining with others until they acquire the necessary weight to precipitate," Correa illustrates.
And she adds: "Why can't those particles join together to flocculate? Because they are electrically charged, so when one particle approaches another, they repel each other and cannot join. What lime does as an ionic product within that medium is to help neutralize that electric charge and allow flocculation, thus serving as a coagulant."
Lime also helps regulate water hardness. "Water hardness is given by the composition of calcium and magnesium carbonates and bicarbonates. If more calcium is introduced, the dissolved carbonate is induced to precipitate to maintain chemical balance. Thus, lime intervenes in regulating water hardness," she specifies.
Sustainable sludges
The treatment of domestic or industrial effluents is a key process for environmental care, either for the good health of natural basins or properties where they are returned, or for the flora and fauna of any ecosystem. In countries where water is a costly and scarce resource, sanitation waters can be reused as drinking water.
Grupo Calidra Cono Sur supplies Chilean sanitation plants with 80% of the total lime the country needs to treat its waters. Lime is used to a greater extent to treat contaminated waters, also called "black waters." And in this process, a virtuous cycle is generated in favor of the land.
What is this treatment like? "Through physical processes, solids are separated from the aqueous phase, some flocculants and other chemicals are added to favor the sedimentation of the remaining suspended particles, and once clarified, the water is returned to the river. These separated solids are treated with lime and reused as fertilizers for agriculture," explains Daniel Rodríguez, Technical Representative, Calidra Chile.
Currently, Chilean water plants have committed to incorporating this sustainable treatment into their sludges in order to operate.
"That is super relevant because ultimately circular economy is being given to a waste. That is, not only are waters recovered that were originally contaminated as black waters and transformed into clean waters that go to natural basins, but also those solids become organic matter that is used to generate agriculture in the southern part of the country," Rodríguez adds.
The use of lime in these sludges has two effects: reaching a highly alkaline pH (between 12 and 13) and reducing the moisture content of the solids (as a side effect). This eliminates bacterial activity, and with it, the odors coming from it, allowing nearby plants to operate without discomfort for the inhabitants. In a second instance, lime also makes it a more malleable material: this sludge turns into a denser and more viscous clay-like substance that can be transported without dripping.
"Originally, sanitation plants were built away from the city because of the odors they emitted. Over the years, and due to the need for land, communities surrounded these plants. So now communities demand that there be no odors. Quimex® is a great ally that prevents odors in sludge," assures Rodríguez.
UN Water Challenges
-2.2 billion people lack access to safely managed drinking water services. (WHO/UNICEF 2019)
-Nearly 2 billion people depend on health care facilities without basic water services (WHO/UNICEF 2020)
-4.2 billion people - more than half of the world's population - lack safely managed sanitation services (WHO/UNICEF 2019)
-297,000 children under five die each year from diarrheal diseases caused by poor sanitation conditions or unsafe water (WHO/UNICEF 2019)
-2 billion people live in countries experiencing water stress (UN 2019).
-90% of natural disasters are water-related (UNISDR)
-80% of wastewater is discharged into the ecosystem without treatment or reuse (UNESCO, 2017)
-Around two-thirds of the world's transboundary rivers lack cooperative management frameworks (SIWI)
-Agriculture accounts for 70% of global water extraction (FAO)